Regular Modifications:
- N-terminal acetylation and/or C-terminal amidation(free of charge):
These modifications can reduce overall charges in peptides, on the other hand, they may reduce the water solubility of peptides as well. Since these terminal modifications may increase the stability of peptides, and make peptides fragments closer to their native states in proteins, they may enhance the biological activities of peptides.
- N-terminal or C-terminal Biotinylation:
Biotinylation has been widely used in immunoassays, which can improve the sensitivity and specificity of the assays. N-term biotinylation can easily been achieved using the carboxyl group of the Biotin to react with the primary amine. In many cases, C-term Biotinylation is also needed, if for example, the free N-term is crucial for activity. Then the C-Biotin will be achieved through adding Lys(Biotin) at the C-terminal.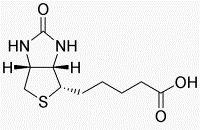
- N-terminal Fatty acid:
Stearic acid,Hexanoic acid,Octanoic acid,Decanoic acid,Palmitic acid,Myristic acid,Lauric acid.
- N-Succinylation






