Here are a few options in the design of the Peptide Library. If you need assistance, please feel free to email us and we will be more than willing to assist you in your library design.
Overlapping Peptide Library
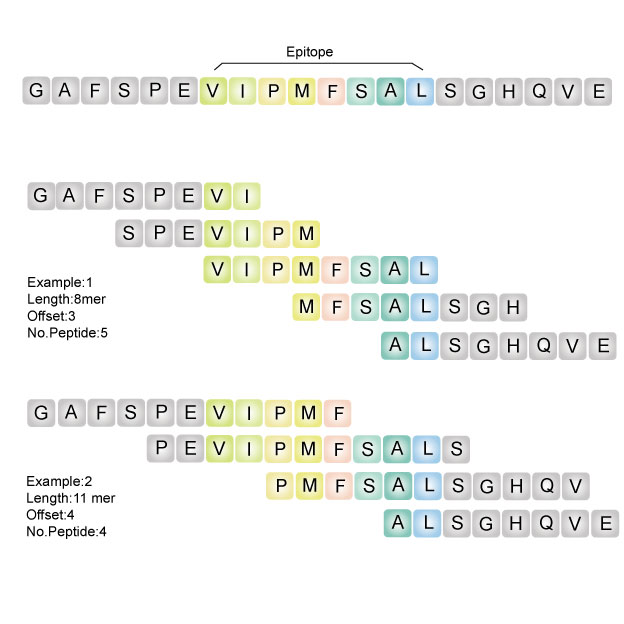
Overlapping Peptide Library that is ideal for T-cell epitope searching can be used for linear and continuous epitope mapping. The original peptide can be subdivided into many overlapping fragments.
Alanine Scanning Library

Alanine scans are useful for identifying essential residues within the peptide. When an essential residue is replaced with alanine, the corresponding peptide shows markedly reduced activity. In alanine scanning libraries, each amino acid in the peptide sequence is individually replaced by alanine.
Truncation Peptide Library
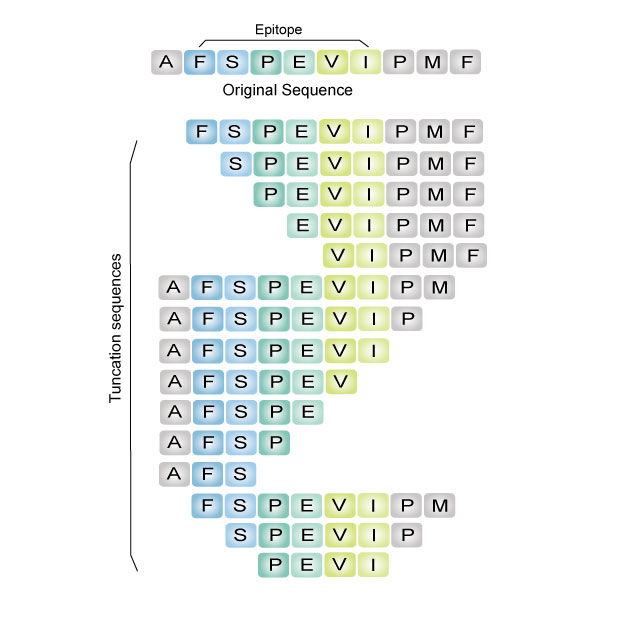
The truncation library can be used to predict the minimum amino acid length required for optimum epitope activity. It can be useful in studying the metabolic degradation of peptide drugs.
Positional Scanning Library

This type of library can help researchers to locate the specific regions responsible for specific effects or activities at certain positions. In positional scanning peptide libraries, every amino acid is systematically substituted into a specified position in a peptide. They are useful for sequence optimization.
Scrambled Peptide Library

The scrambled peptides are typically used as negative controls to show that a specific sequence is critical to the protein function or activity. It is also a random screening tool used to find new leads.






